The SMPP DCS field (and SMPP character encoding)
This page offers information on how to encode the SMPP DCS field.
How does Ozeki SMS Gateway encode the SMPP DCS field
In most scenarios you don't have to manually configure the DCS field of SMPP PDUs. Ozeki SMS Gateway does this for your. To control how Ozeki SMS Gateway does the encoding, you can configure the default aphabet on the SMPP Client configuration form (Figure 1).
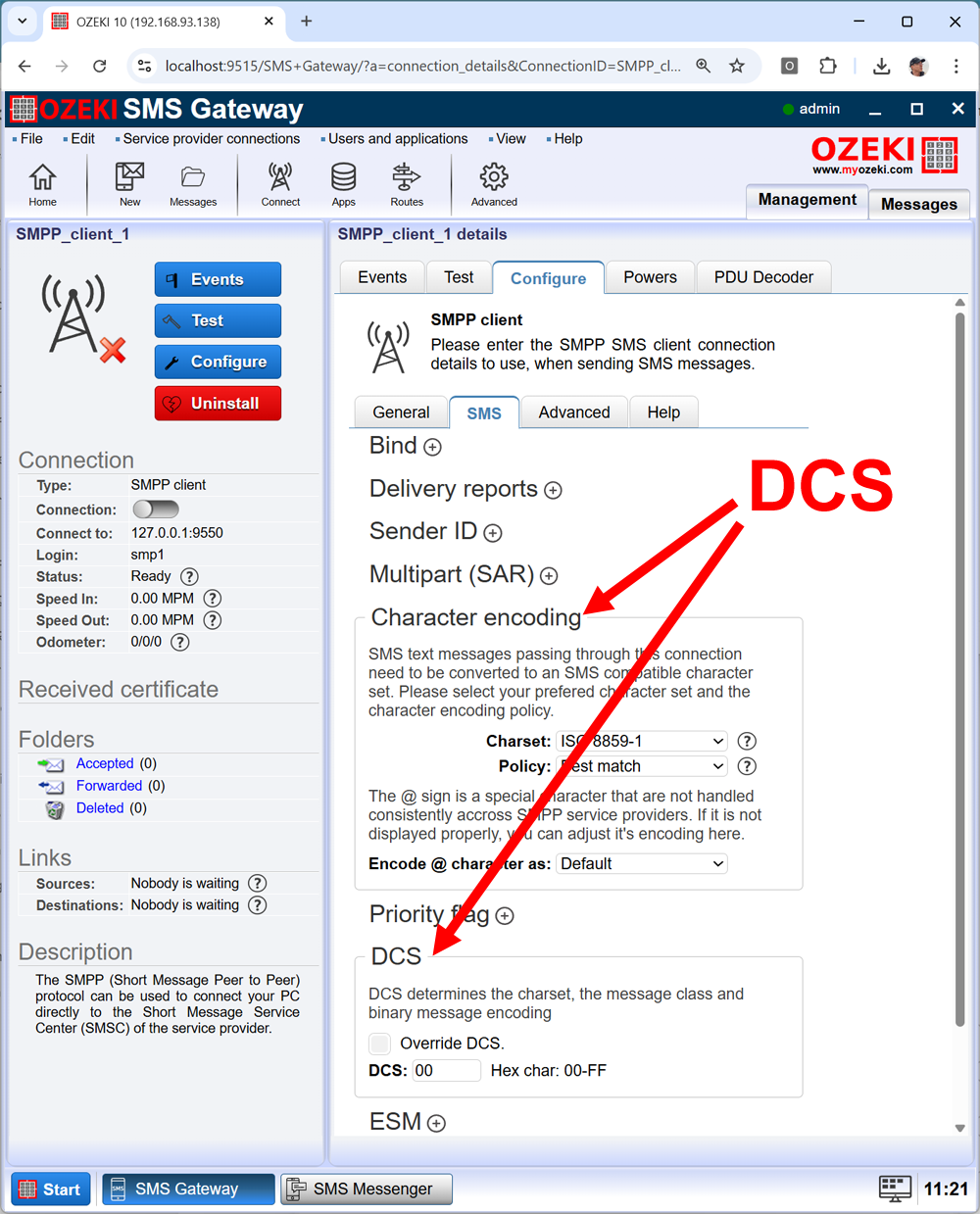
On this form, you can set the preferred character set, or you can ask Ozeki SMS Gateway to use a fix value for the DCS parameter in the SMS PDU.
What is the SMPP DCS Field?
The Data Coding Scheme (DCS) in SMPP (Short Message Peer-to-Peer Protocol) is a 1-byte field within SMPP PDUs (Protocol Data Units). It defines how the message payload is encoded, enabling proper interpretation by the receiving entity. The DCS specifies:
- Character encoding (e.g., GSM-7, UCS2, 8-bit binary)
- Message class (e.g., Flash SMS)
- Compression flags
DCS Structure and Bitmask
The DCS is a bitmask where each bit group serves a specific purpose:
| Bits | Description |
|---|---|
| 7-6 | Coding Group: Determines the general encoding type. |
| 5-4 | Alphabet: Specifies the character set (if Coding Group = 00). |
| 3-0 | Message Class/Flags: Indicates message type (e.g., Flash) or compression. |
Coding Group Values
| Coding Group (Bits 7-6) | Description |
|---|---|
| 00 | General Data Coding (alphabet specified in bits 5-4) |
| 01 | Reserved |
| 10 | UCS2 Encoding (16-bit) |
| 11 | Data Coding/Message Class (e.g., Flash SMS) |
Example DCS Values
| DCS (Hex) | Description | Binary |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | GSM-7 Default Alphabet | 00000000 |
| 0x04 | 8-bit Binary Data | 00000100 |
| 0x08 | UCS2 (Unicode) | 00001000 |
| 0x10 | Flash SMS (GSM-7) | 00010000 |
| 0xF0 | Flash SMS (UCS2) | 11110000 |
Example SMPP PDUs with DCS
Example 1: SubmitSM with GSM-7 Encoding (DCS=0x00)
0000001D // Command Length (29 bytes)
00000004 // Command ID (SubmitSM)
00000001 // Sequence Number
00 // Source TON
00 // Source NPI
736F7572636500 // Source Address ("source")
00 // Dest TON
00 // Dest NPI
36353433323100 // Destination Address ("654321")
00 // ESM Class
00 // Protocol ID
00 // Priority
00 // Schedule Delivery Time
00 // Validity Period
00 // Registered Delivery
00 // Replace-if-Present
00 // Data Coding (DCS=0x00)
00 // SM Default Message ID
07 // SM Length (7 septets)
C8329BFD06DDDF72 // Short Message ("Hello!")
Example 2: SubmitSM with UCS2 Encoding (DCS=0x08)
00000024 // Command Length (36 bytes)
00000004 // Command ID (SubmitSM)
00000002 // Sequence Number
00 // Source TON
00 // Source NPI
736F7572636500 // Source Address ("source")
00 // Dest TON
00 // Dest NPI
36353433323100 // Destination Address ("654321")
00 // ESM Class
00 // Protocol ID
00 // Priority
00 // Schedule Delivery Time
00 // Validity Period
00 // Registered Delivery
00 // Replace-if-Present
08 // Data Coding (DCS=0x08)
00 // SM Default Message ID
0C // SM Length (12 bytes)
00480065006C006C006F0021 // "Hello!" in UCS2
Example 3: Flash SMS (DCS=0x10)
0000001D // Command Length (29 bytes)
00000004 // Command ID (SubmitSM)
00000003 // Sequence Number
00 // Source TON
00 // Source NPI
736F7572636500 // Source Address ("source")
00 // Dest TON
00 // Dest NPI
36353433323100 // Destination Address ("654321")
00 // ESM Class
00 // Protocol ID
00 // Priority
00 // Schedule Delivery Time
00 // Validity Period
00 // Registered Delivery
00 // Replace-if-Present
10 // Data Coding (DCS=0x10: Flash SMS)
00 // SM Default Message ID
07 // SM Length (7 septets)
C8329BFD06DDDF72 // Short Message ("Hello!")
Conclusion
The DCS field is critical for ensuring SMS messages are encoded and displayed correctly. Implementations may vary, so consult the SMPP specification (v3.4 or v5.0) for precise bitmask details. Proper use of DCS avoids encoding errors and ensures compatibility across SMSCs.
