How to Send SMS through the SMPP API using Python
The SMPP API (Short Message Peer-to-Peer) is a powerful protocol for exchanging SMS messages between External Short Message Entities (ESMEs) and Short Message Service Centers (SMSCs). For developers using the Ozeki SMS Gateway, leveraging the SMPP API with Python enables seamless SMS integration for applications. This comprehensive guide provides step-by-step instructions, practical Python code examples, and best practices for establishing, maintaining, and using an SMPP API connection to send SMS messages efficiently.
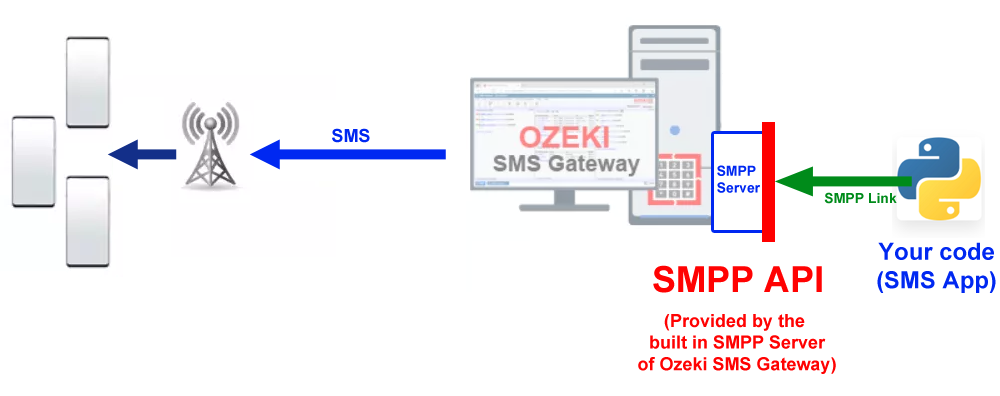
Why Use Python with SMPP API for SMS Messaging?
Python’s simplicity and robust libraries, such as smpplib, make it
an ideal choice for integrating with the SMPP API. The SMPP protocol allows for
high-performance SMS delivery, real-time delivery reports, and reliable connection
management. By combining Python with the SMPP API, developers can create scalable
SMS solutions for applications like notifications, marketing campaigns, or
two-factor authentication (2FA).
How to Send SMS through the SMPP API using Python (Quick Steps)
- Verify SMPP Credentials: Ensure you have the correct host, port, username, and password for your SMPP user in Ozeki SMS Gateway.
- Write and Execute Python Code: Use the
smppliblibrary to create a script for connecting to the SMPP server and sending SMS. - Check Results: Confirm successful message delivery through logs in the Ozeki SMS Gateway interface.
How to Send SMS through the SMPP API using Python (Video tutorial)
Watch this step-by-step video tutorial to learn how to send SMS messages using
Python and the SMPP API with Ozeki SMS Gateway. The tutorial covers setting up
an SMPP user, connecting with the smpplib library, sending messages,
maintaining connections, and handling delivery reports.
Step-by-Step Guide to Sending SMS with Python and SMPP API
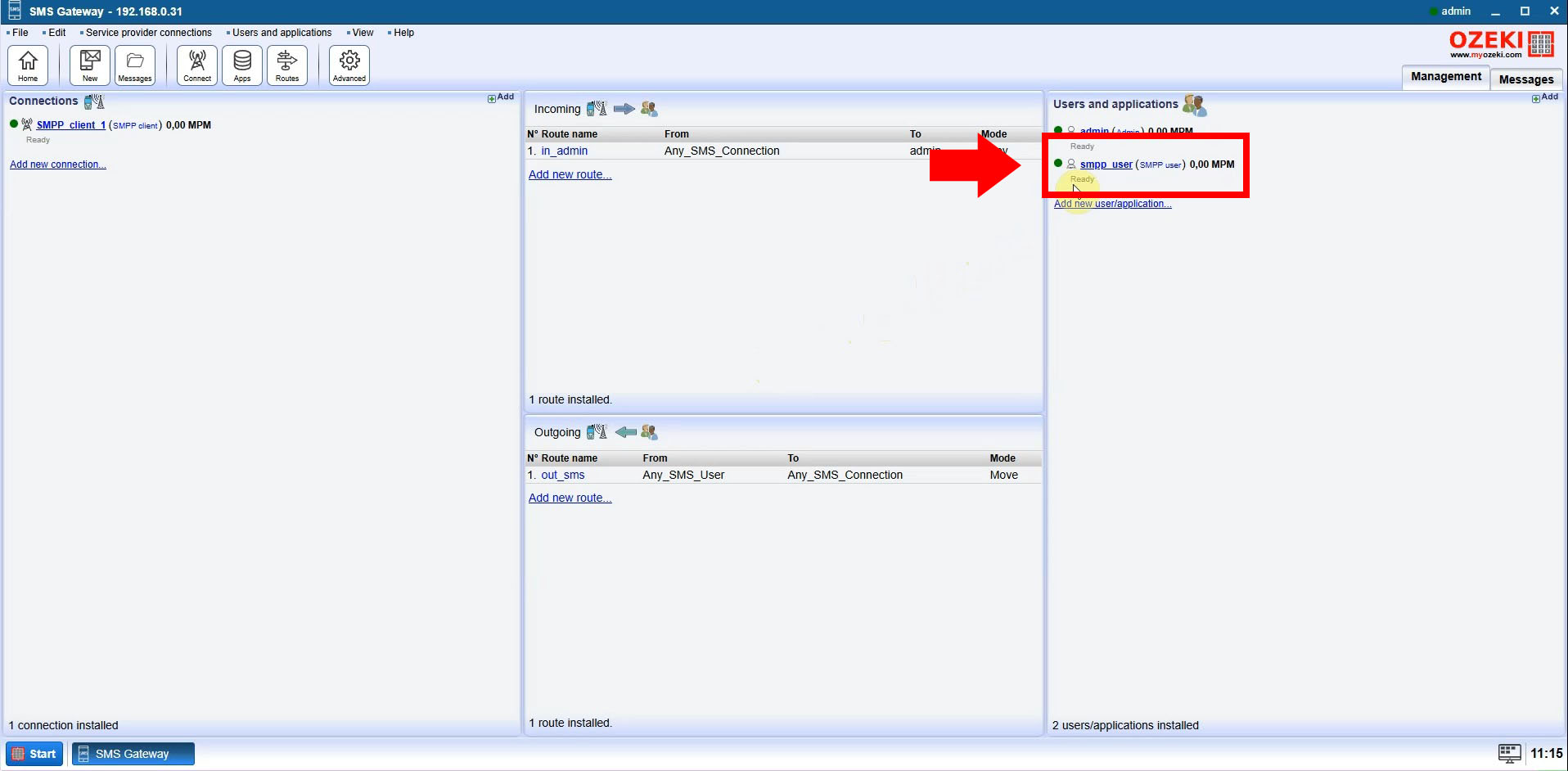
Step 1: Select Your SMPP User
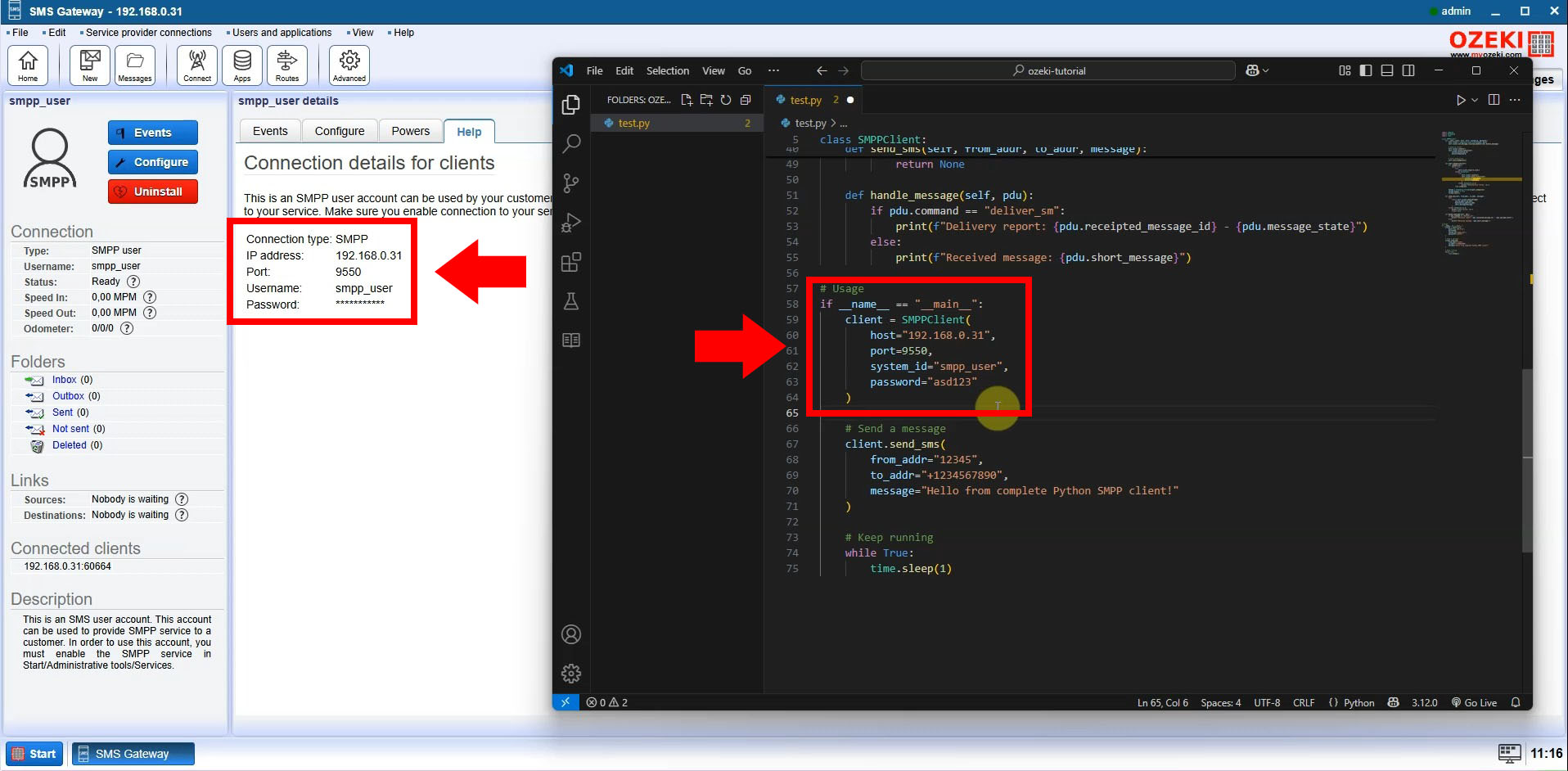
In the Ozeki SMS Gateway interface, navigate to the "Users and Applications" section. Select or create an SMPP user to establish a connection from your Python script. This user will authenticate your application with the SMPP server.
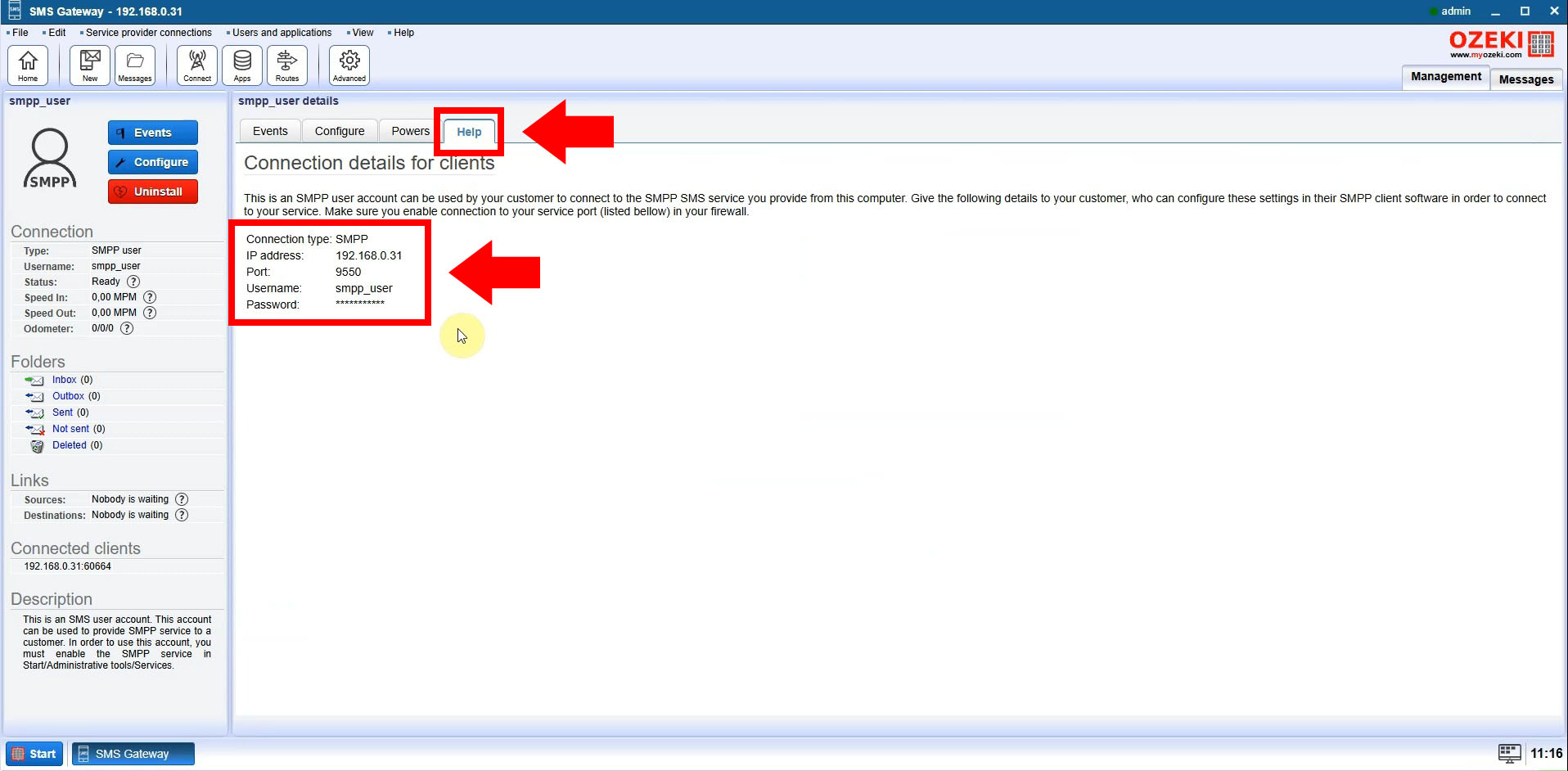
Step 2: Retrieve Connection Details
After selecting your SMPP user, go to the "Help" tab in the Ozeki SMS Gateway interface. Here, you’ll find essential connection details, including the IP address, port number, username, and password. These credentials are critical for configuring your Python script to connect to the SMPP server.
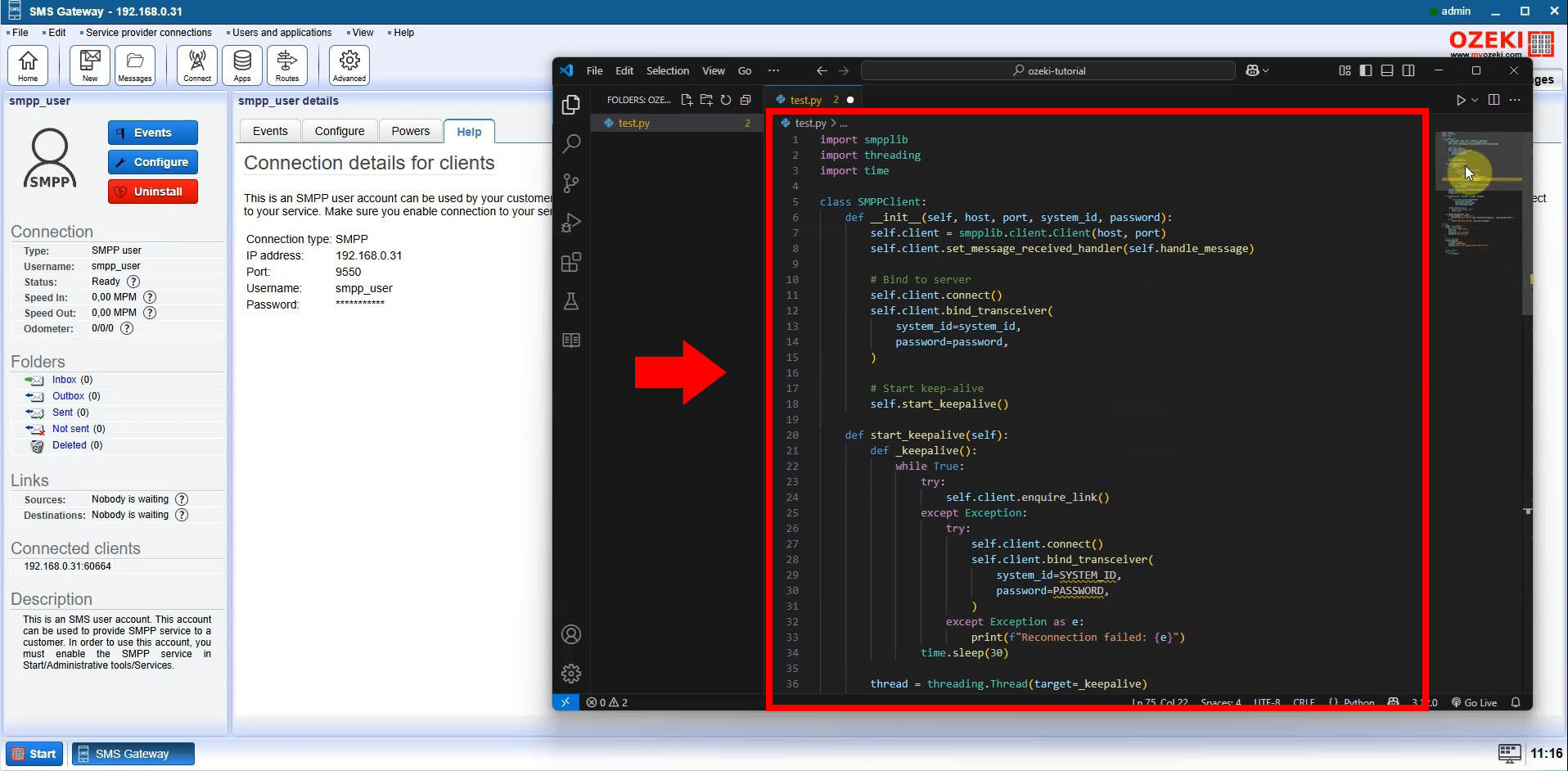
Step 3: Write the Python SMPP Code
Open your preferred Python IDE or editor and paste the SMPP connection code provided
below. This code uses the smpplib library to establish a connection
with the Ozeki SMS Gateway and prepare the environment for sending SMS messages.
Step 4: Update SMPP Credentials
Replace the placeholder values in the Python code (host, port, username, password, and phone numbers) with your actual SMPP credentials and the recipient’s phone number. This ensures your script connects to the correct SMPP server and sends messages to the intended recipient.
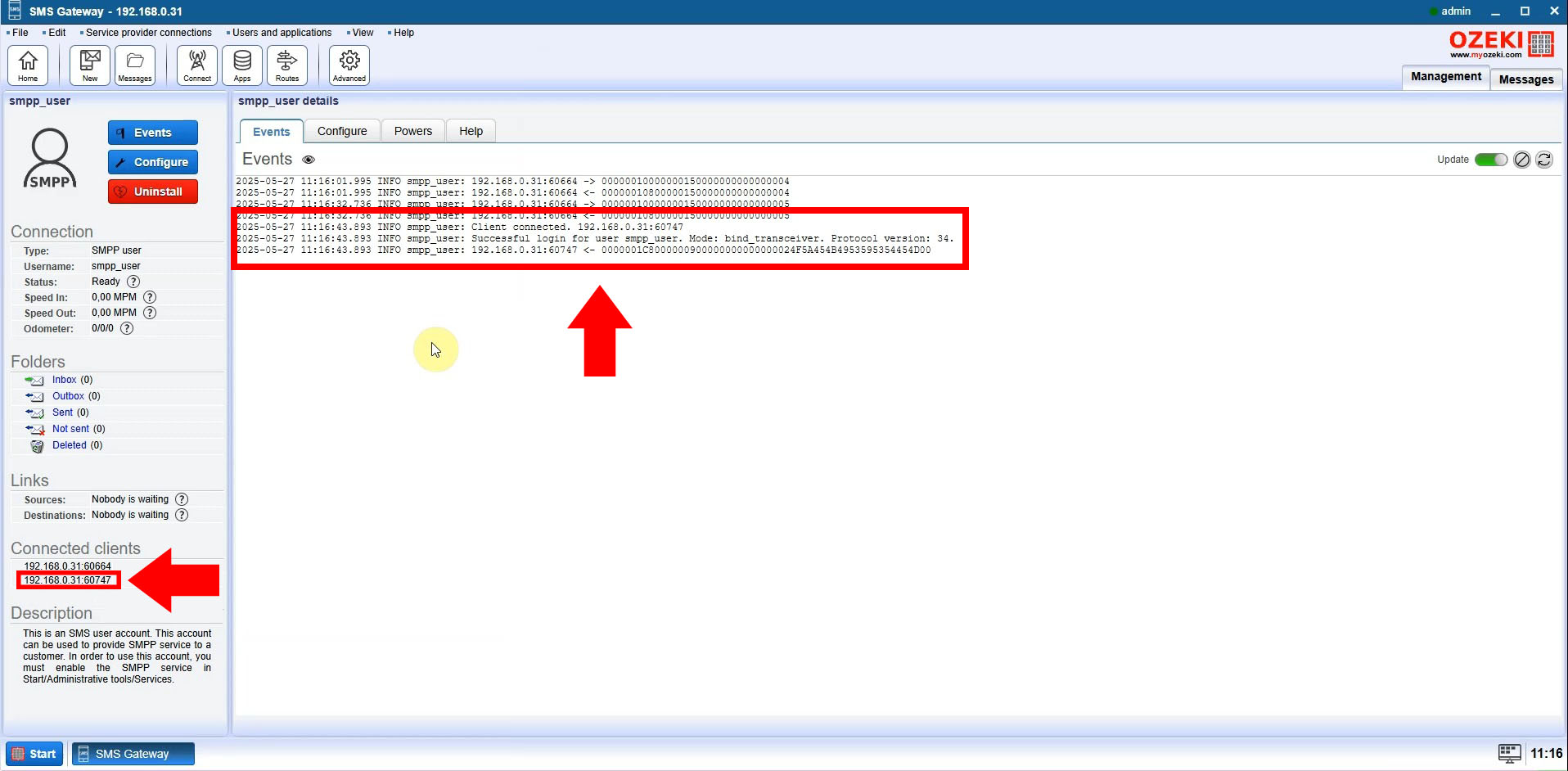
Step 5: Verify Successful Connection
Run your Python script. If configured correctly, the Ozeki SMS Gateway interface will log a successful connection for your SMPP user. This confirms that your Python script is ready to send SMS messages via the SMPP API.
How to Establish an SMPP API Connection in Python for SMS Messaging
To send SMS messages using the SMPP API, you must first set up an SMPP user
in Ozeki SMS Gateway and bind your Python client to the SMPP server.
The smpplib library simplifies this process by handling low-level protocol details.
Below is a Python code example for establishing an SMPP connection:
import smpplib
# SMPP connection parameters
HOST = 'your.ozeki.server'
PORT = 2775
SYSTEM_ID = 'your_username'
PASSWORD = 'your_password'
# Initialize SMPP client
client = smpplib.client.Client(HOST, PORT)
# Bind as transmitter for sending SMS
client.connect()
client.bind_transmitter(
system_id=SYSTEM_ID,
password=PASSWORD,
)
print("Successfully connected to the SMPP server using Python")
Key SMPP Protocol Data Units (PDUs)
The SMPP protocol relies on Protocol Data Units (PDUs) to manage connections and messaging. Below is a table summarizing the key PDUs used in Python for SMPP API integration:
| PDU | Python Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
bind_transmitter |
client.bind_transmitter() |
Initiates a connection for sending SMS messages |
bind_receiver |
client.bind_receiver() |
Establishes a connection for receiving SMS messages |
bind_transceiver |
client.bind_transceiver() |
Enables bidirectional SMS messaging (send and receive) |
Maintaining a Stable SMPP API Connection in Python for SMS Sending
SMPP connections require periodic "keep-alive" signals to prevent timeouts.
The enquire_link PDU is sent every 30 seconds to maintain the connection.
Below is a Python example using a threading approach to send keep-alive signals:
import time
import threading
def send_enquire_link():
while True:
try:
client.enquire_link()
print("Sent enquire_link PDU to maintain SMPP connection")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error sending enquire_link: {e}")
time.sleep(30) # Send every 30 seconds
# Start keep-alive thread
keepalive_thread = threading.Thread(target=send_enquire_link)
keepalive_thread.daemon = True
keepalive_thread.start()
Sending SMS with Python through the SMPP API
Once the connection is established, you can send SMS messages using the submit_sm
PDU. The following Python code demonstrates how to send an SMS and handle the
response:
def send_sms(source_addr, destination_addr, message):
try:
# Send submit_sm PDU
pdu = client.send_message(
source_addr_ton=smpplib.consts.SMPP_TON_INTL,
source_addr_npi=smpplib.consts.SMPP_NPI_ISDN,
source_addr=source_addr,
dest_addr_ton=smpplib.consts.SMPP_TON_INTL,
dest_addr_npi=smpplib.consts.SMPP_NPI_ISDN,
destination_addr=destination_addr,
short_message=message,
data_coding=0x00, # GSM 7-bit encoding
)
print(f"SMS sent successfully, message_id: {pdu.message_id}")
except smpplib.exceptions.PDUError as e:
print(f"SMPP PDU error: {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error sending SMS: {e}")
# Example usage
send_sms(
source_addr="12345",
destination_addr="+1234567890",
message="Hello from Python SMPP client!"
)
Handling SMS Delivery Reports in Python
To track the delivery status of sent SMS messages, you can handle delivery reports
using the deliver_sm PDU. Below is a Python example for processing
delivery reports:
def handle_delivery_report(pdu):
print(f"Received delivery report for message {pdu.receipted_message_id}")
print(f"Status: {pdu.message_state}")
# Set up delivery report handler
client.set_message_received_handler(lambda pdu: handle_delivery_report(pdu))
Complete Python SMPP API Client Example for Sending SMS
Below is a complete, production-ready Python script that integrates with the SMPP API to send SMS messages, maintain a stable connection, and handle delivery reports:
import smpplib
import threading
import time
class SMPPClient:
def __init__(self, host, port, system_id, password):
self.client = smpplib.client.Client(host, port)
self.client.set_message_received_handler(self.handle_message)
# Bind to SMPP server
self.client.connect()
self.client.bind_transceiver(
system_id=system_id,
password=password,
)
# Start keep-alive thread
self.start_keepalive()
def start_keepalive(self):
def _keepalive():
while True:
try:
self.client.enquire_link()
print("Keep-alive signal sent")
except Exception:
try:
self.client.connect()
self.client.bind_transceiver(
system_id=system_id,
password=password,
)
print("Reconnected to SMPP server")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Reconnection failed: {e}")
time.sleep(30)
thread = threading.Thread(target=_keepalive)
thread.daemon = True
thread.start()
def send_sms(self, from_addr, to_addr, message):
try:
return self.client.send_message(
source_addr=from_addr,
destination_addr=to_addr,
short_message=message,
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"SMS send failed: {e}")
return None
def handle_message(self, pdu):
if pdu.command == "deliver_sm":
print(f"Delivery report: {pdu.receipted_message_id} - {pdu.message_state}")
else:
print(f"Received message: {pdu.short_message}")
# Usage example
if __name__ == "__main__":
client = SMPPClient(
host="your.ozeki.server",
port=2775,
system_id="your_username",
password="your_password"
)
# Send an SMS
client.send_sms(
from_addr="12345",
to_addr="+1234567890",
message="Hello from Python SMPP client!"
)
# Keep the script running
while True:
time.sleep(1)
Best Practices for SMPP API Integration with Python
- Error Handling: Always implement robust exception handling to manage connection failures, PDU errors, and timeouts.
- Connection Re-establishment: Include logic to reconnect automatically if the SMPP connection drops.
- Logging: Log connection status, sent messages, and delivery reports for debugging and monitoring.
- Security: Store SMPP credentials securely, using environment variables or a configuration file.
- Scalability: For high-volume SMS applications, consider using asynchronous libraries or connection pooling.
Conclusion
This guide has provided a detailed walkthrough for integrating the
SMPP API with Python using the Ozeki SMS Gateway.
By leveraging the smpplib library, developers can establish reliable
SMPP connections, send SMS messages, and handle delivery reports with ease. The
provided Python code examples and best practices ensure robust and scalable SMS
applications for various use cases, from notifications to marketing campaigns.
Note: For production environments, enhance the provided code with comprehensive error handling, reconnection logic, and logging to ensure maximum reliability and performance.
More information
- How to set up an SMPP API client connection with Your SMSC
- How to set up an SMPP API server to send ad receive SMS from multiple Apps
- How to choose the right SMPP API provider for your business
- How to Send SMS Using the SMPP API at the protocol level
- How to Send SMS through the SMPP API using Python
- How to Send SMS through the SMPP API using Javascript
- How to send SMS through the SMPP API using Java
- How to Send SMS through the SMPP API using PHP
- How to Send SMS through the SMPP API using C#
- How to Send SMS through the SMPP API using C/Cpp
- How to Receive SMS using the SMPP API
- How to Receive an SMS Delivery Report using the SMPP API
- SMPP API FAQ
