How to schedule an SMS in Kotlin
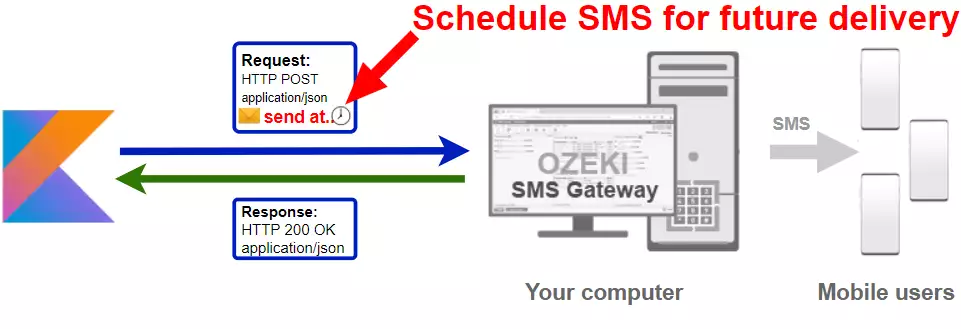
The simplest way to send SMS from Kotlin is to use the built in HTTP/Rest SMS api of Ozeki SMS Gateway. When you use this API, you will send SMS messages by issuing a HTTP Post request to the SMS gateway. The HTTP Post request will contain a message formatted in json format. The SMS gateway will send this SMS to the recipient phone, and it will return a HTTP 200 OK response to your request. (Figure 1)
Kotlin code to send a scheduled sms to mobile
The Kotlin sms code sample below demonstrates how you can send a scheduled SMS using the http rest sms api of Ozeki SMS Gateway using the Kotlin Ozeki.Libs.Rest library. This library is provided to you free of charge, and you may use it and modify it in any of your projects.
MainActivity.kt
package send.scheduledsms
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import Ozeki.Libs.Rest.Configuration
import Ozeki.Libs.Rest.MessageApi
import Ozeki.Libs.Rest.Message
import android.text.method.ScrollingMovementMethod
import kotlinx.coroutines.Dispatchers
import kotlinx.coroutines.GlobalScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val inputToAddress:android.widget.EditText = findViewById(R.id.inputToAddress)
val inputMessage:android.widget.EditText = findViewById(R.id.inputMessage)
val date:android.widget.EditText = findViewById(R.id.inputTimeToSendDate)
val time:android.widget.EditText = findViewById(R.id.inputTimeToSendTime)
val btnSendRequest:android.widget.Button = findViewById(R.id.btnSendRequest)
val logBox:android.widget.TextView = findViewById(R.id.logBox)
logBox.movementMethod = ScrollingMovementMethod()
val configuration = Configuration(
username = "http_user",
password = "qwe123",
apiurl = "http://10.0.2.2:9509/api"
)
val api = MessageApi(configuration)
btnSendRequest.setOnClickListener {
if (inputToAddress.text.toString() != "" && inputMessage.text.toString() != ""
&& date.text.toString() != "" && time.text.toString() != "") {
val datetime = String.format("%s %s", date.text.toString(), time.text.toString())
val msg = Message()
msg.ToAddress = inputToAddress.text.toString()
msg.Text = inputMessage.text.toString()
msg.TimeToSend = datetime
GlobalScope.launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
val response = api.Send(msg)
logBox.text = String.format("%s\n%s", logBox.text, response.toString())
}
inputToAddress.text.clear()
inputMessage.text.clear()
date.text.clear()
time.text.clear()
}
}
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnSendRequest"
android:layout_width="320dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="36dp"
android:text="Send"
android:backgroundTint="#FF3F3F"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.494"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/logBox" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textToAddress"
android:layout_width="320dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="36dp"
android:text="To address:"
android:textSize="20sp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.498"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textMessage"
android:layout_width="320dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="Message:"
android:textSize="20sp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.505"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/inputToAddress" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textWhen"
android:layout_width="320dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="Time to send:"
android:textSize="20sp"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.494"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/inputMessage" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputToAddress"
android:layout_width="320dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="+36201111111"
android:inputType="textPersonName"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.505"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/textToAddress" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputMessage"
android:layout_width="320dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:ems="10"
android:gravity="start|top"
android:hint="Hello world!"
android:inputType="textMultiLine"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.505"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/textMessage" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputTimeToSendTime"
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="44dp"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="15:30:00"
android:inputType="time"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/textWhen" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/logBox"
android:layout_width="320dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:scrollbars="vertical"
android:text="Logs:"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.505"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/inputTimeToSendTime" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/inputTimeToSendDate"
android:layout_width="180dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="24dp"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="2021-06-16"
android:inputType="date"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/inputTimeToSendTime"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="1.0"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/textWhen" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
How to use the Kotlin sms example:
You can use the Message class to create the SMS and you can use the MessageApi class to send the scheduled SMS to the SMS gateway. The SMS gateway will forward your message to the mobile network either through a wireless connection or through the Internet.
Download SendScheduledSms.kt
The source code explained in this article can be downloaded and used and modified free of charge.
Download: SendScheduledSms.kt.zip (149Kb)
What is in the SendScheduledSms.kt.zip file?
The SendScheduledSms.kt.zip file contains the an example project, which has the Ozeki.Libs.Rest library in it. With this library you can send, delete, mark and receive sms messages by creating a MessageApi and using the Send(), Delete(), Mark(), and Receive() methods. (Figure 2)
How to send a scheduled SMS from Kotlin(Quick steps)
To send a scheduled sms from Kotlin:
- Install Ozeki SMS Gateway
- Connect Ozeki SMS Gateway to the mobile network
- Send a test sms from Ozeki GUI
- Create a HTTP sms api user
- Android Studio
- Download the example project above
- Create the SMS by creating a new Message object
- Create an api to send your scheduled message
- Use the Send method to send your scheduled message
- Read the response message on the console
- Check the logs in the SMS gateway
Install Ozeki SMS Gateway and create an HTTP API user
To be able to send SMS from Kotlin, first you need to install Ozeki SMS Gateway. The SMS gateway can be installed on the same computer, where you develop your Kotlin code in Android Studio. After installation, the next step is to connect Ozeki SMS Gateway to the mobile network. You can send a test sms from the Ozeki GUI to verify, that your mobile network connection works. The final step to prepare your environment is to create a HTTP sms api user. Create a user with a username of "http_user", and with a password of "qwe123" to make the example work without modification.
After the environment is setup, you can run your Kotlin code.
HTTP API url to use send sms from Kotlin
To send a scheduled SMS from Kotlin, your Kotlin will have to issue an HTTP request to the SMS gateway. The API url is shown below. Note that the IP address (127.0.0.1) should be replaced to the IP address of your SMS gateway. If Ozeki SMS Gateway is installed on the same computer where the JavaScript sms application is running, this can be 127.0.0.1. If it is installed on a different computer, it should be the IP address of that computer.
http://127.0.0.1:9509/api?action=rest
HTTP authentication to use send a scheduled sms from Kotlin
To authenticate the Kotlin sms client, you need to send the username and password in a base64 encoded string to the server in a HTTP request. The format used is: base64(username+":"+password). In Kotlin you can use the following code to do this encoding:
var usernamePassword = "%s:%s".format(username, password) return "Basic %s".format(Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(usernamePassword.toByteArray()))
For example, if you encode the username 'http_user' and the password 'qwe123', you will get the following base64 encoded string: aHR0cF91c2VyOnF3ZTEyMw==. To send
HTTP request header to send SMS from Kotlin
To send the SMS messages, you need to include the following lines as headers in the HTTP request. Note that we include a content type and an Authorization header.
Content-Type: application/json Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ==
HTTP request to send SMS from Kotlin
To submit the SMS, your Kotlin application will send an HTTP request similar to the one below. Note, that this request contains a HTTP header part and a http body part. The HTTP body is a JSON encoded data string. It contains the recipient's number and the message's text.
POST /api?action=sendmsg HTTP/1.1
Connection: Keep-Alive
Content-Length: 320
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Accept-Encoding: gzip
Authorization: Basic aHR0cF91c2VyOnF3ZTEyMw==
Host: 10.0.2.2:9509
User-Agent: okhttp/4.2.2
{
"messages": [
{
"message_id": "e68f8e11-dce2-48e2-a2c5-1d2efa98272a",
"to_address": "+36201111111",
"text": "Hello world!",
"create_date": "2021-06-17T15:04:03",
"valid_until": "2021-06-24T15:04:03",
"time_to_send": "2021-06-17 15:10:00",
"submit_report_requested": true,
"delivery_report_requested": true,
"view_report_requested": true
}
]
}
HTTP response received by the Kotlin sms example
Once the SMS gateway receives this request, it will generate a HTTP response. The HTTP response will contain a status code, to indicate whether the SMS submit request was successful or not. It will also return a JSON encoded structure to provide you useful details about the message's submission.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
User-Agent: OZEKI 10.3.120 (www.myozeki.com)
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf8
Last-Modified: Thu, 17 Jun 2021 14:56:26 GMT
Server: 10/10.3.120
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
{
"http_code": 200,
"response_code": "SUCCESS",
"response_msg": "Messages queued for delivery.",
"data": {
"total_count": 1,
"success_count": 1,
"failed_count": 0,
"messages": [
{
"message_id": "e68f8e11-dce2-48e2-a2c5-1d2efa98272a",
"from_station": "%",
"to_address": "+36201111111",
"to_station": "%",
"text": "Hello world!",
"create_date": "2021-06-17 15:04:03",
"valid_until": "2021-06-24 15:04:03",
"time_to_send": "2021-06-17 15:10:00",
"submit_report_requested": true,
"delivery_report_requested": true,
"view_report_requested": false,
"tags": [
{
"name": "Type",
"value": "SMS:TEXT"
}
],
"status": "SUCCESS"
}
]
}
}
How to send a scheduled SMS from Kotlin using the sms api and the example project above (Video tutorial)
This video shows you how to download and use the SendScheduledSms.kt project. Once you opened the example project, you might notice that a there is a package called Ozeki.Libs.Rest This is the package that contains the MessageApi and all the stuffs you need to send a scheduled SMS using Kotlin.
How to check that the SMS has been accepted by the HTTP user
After the SMS has been submitted, it is a good idea to check your SMS gateway, to see what it has received. You can check the log by opening the HTTP user's details from the Ozeki SMS Gateway management console. At the end of the video above you can see how to check if the request has been received by the http_user.
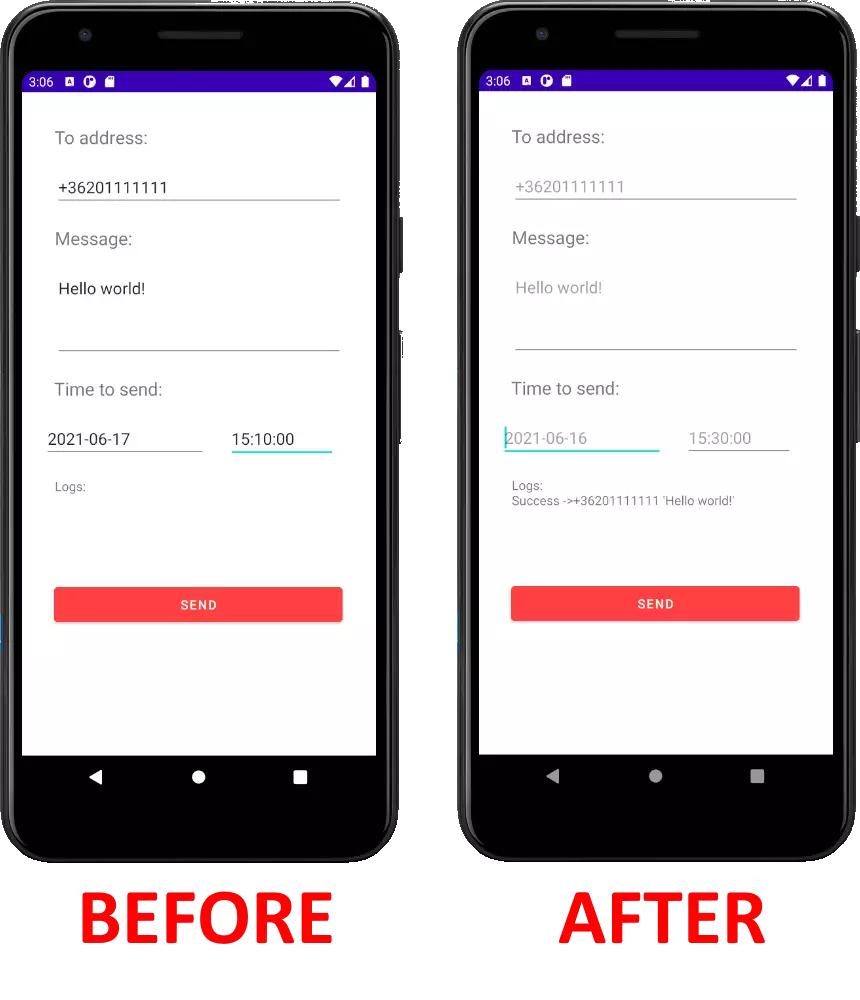
How using the app looks like on a Phone (Video tutorial)
On Figure 4, you can see the user interface of the app on a phone. As you can see on the before-after pictures, scheduled SMS sending is very easy with this app. After the message was sent, the log of the sending process will be visible under the 'Time to send' textbox. You can get all the information about the sent message here.
How to add Ozeki.Libs.Rest to your own project
The Ozeki.Libs.Rest library can be downloaded and used and modified free of charge.
Download: Ozeki.Libs.Rest.kt.zip (7.66Kb)
If you decide to create your application on your own only with the Ozeki.Libs.Rest
library, there are few things you should change in your base application.
In order to use the Ozeki.Libs.Rest library you have to put it into the java fodlder
of the main directory
In the following video I will show you how to download and add the Ozeki.Libs.Rest
library to your own project.
Dependencies
It is important to mention, that the Ozeki.Libs.Rest library has some dependencies. In order to use it you have to add these dependencies into the Gradle Scripts.
implementation "com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:4.2.2" implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.5.0' implementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:1.5.0'
Adding dependencies to the project (Video tutorial)
In the following video, you will learn how to add the previously mentioned dependencies. It will start with copying the code and will guide you to the successfully attached dependencies. The video is only 53 seconds long, but it contains all the needed actions to finish the process. You can follow this tutorial without any effort made.
Internet access
In order to make it possible for your application to send
an HTTP request, you have to enable your application
to connect to the internet.
In the following video I'll show you how to enable internet access
for your Kotlin application.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
android:usesCleartextTraffic="true"
Enabling internet connection for your project (Video tutorial)
You need to add both of these lines to the AndroidManifest.xml file. In the following video I'll show you where you should put the codes above. You need to add both of these lines to the AndroidManifest.xml file. In the following video, I'll show you where you should put the codes above. The video will start with copying and pasting the code, and will take you to the successfully added internet connection. This video is detailed and offers an easy time following it.
Summary
This guide shows you the steps of scheduling SMS in Kotlin with the HTTP user of the Ozeki SMS Gateway. Scheduling SMS to deliver the messages when your customers have the time to read them is really helps you to maintain a good relationship with them. To care about the little things like finding the perfect timing for share thoughts and information is essential if you want to show how professional your business is.
Continue reading tutorials like this on the Ozeki webpage. There is more information about using Kotlin for operating with SMS messages, next learn How to receive an SMS in Kotlin.
Download the Ozeki SMS Gateway now and use what you have learned!
