How to configure the SMPP ESM Class field
Ozeki SMS Gateway ESM class settings
Ozeki SMS Gateway allows you to manually configure the ESM class field (Figure 1)
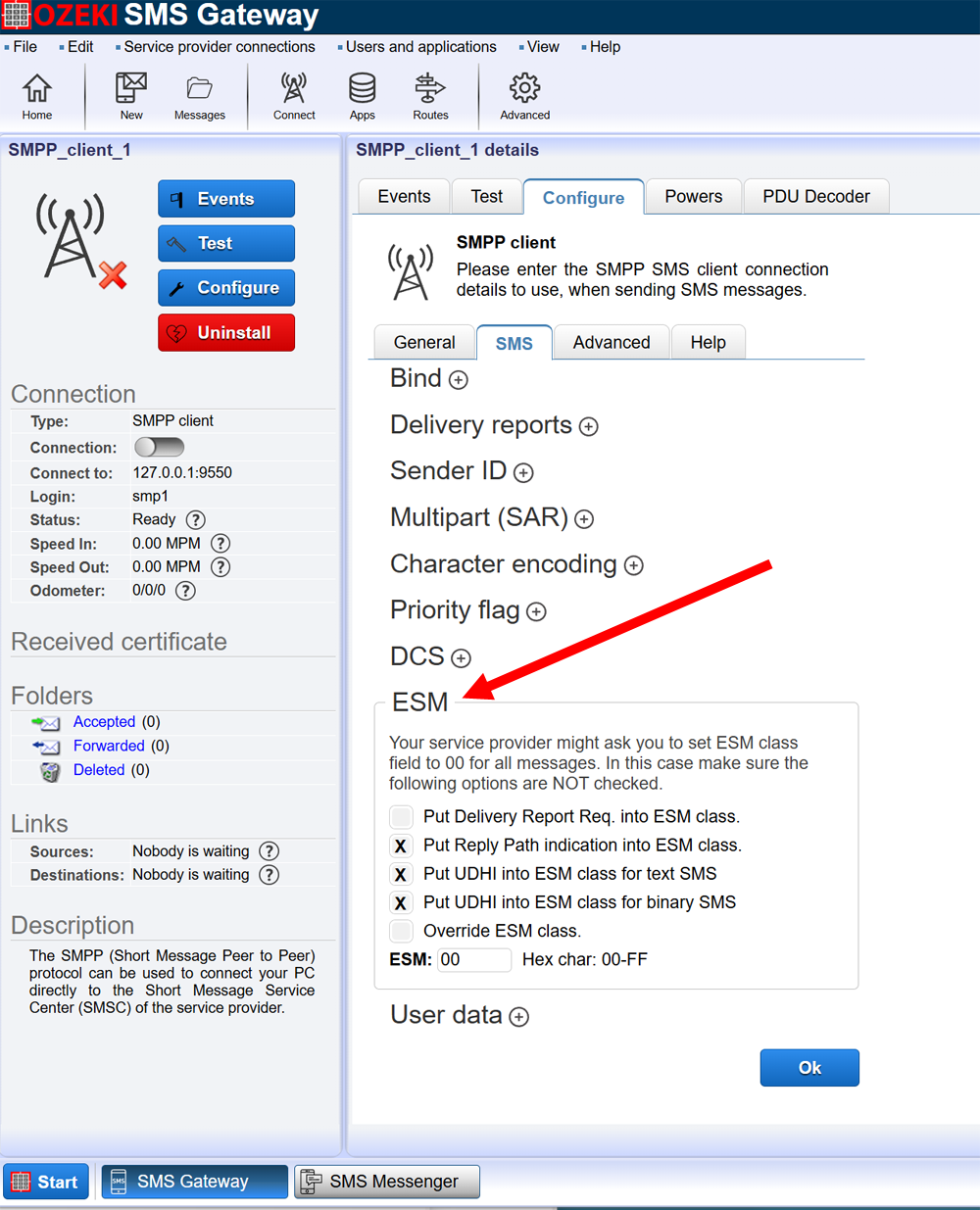
What is the ESM Class Field?
The Extended Service Message (ESM) Class in SMPP is a 1-byte field in SMPP PDUs that controls advanced message handling features.
It is used in submit_sm, deliver_sm, and data_sm operations to specify:
- Message types (e.g., SMS, delivery receipt)
- Delivery receipt behavior
- UDH (User Data Header) presence
- Message priority and routing flags
ESM Class Structure and Bitmask
The ESM class is a bitmask where each bit or group of bits activates specific features:
| Bits | Description |
|---|---|
| 7 | Messaging Mode: 0 = Default, 1 = Datagram |
| 6 | Message Type: 0 = Normal, 1 = Delivery Receipt |
| 5 | UDHI Indicator: 1 = UDH present in payload |
| 4 | Reply Path: 1 = Reply path requested |
| 3-2 | Message Priority (00 = Normal, 01 = Interactive, 10 = Urgent, 11 = Emergency) |
| 1-0 | Reserved |
Common ESM Class Values
| ESM (Hex) | Binary | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | 00000000 | Default (no special handling) |
| 0x04 | 00000100 | UDHI flag set (UDH present) |
| 0x08 | 00001000 | Reply path requested |
| 0x20 | 00100000 | Delivery receipt (bit 6 = 1) |
| 0x30 | 00110000 | Urgent priority + delivery receipt |
| 0x60 | 01100000 | Datagram mode + delivery receipt |
Key Use Cases
1. Concatenated SMS (UDHI Flag)
When sending multipart messages, set bit 5 (UDHI=1) and include a User Data Header (UDH) in the payload. Example for a 3-part message:
ESM Class: 0x40 (binary 01000000: UDHI enabled)
Payload:
05 00 03 02 01 // UDH (5 bytes: IEI=00, IEDL=03, part 1 of 2)
C8329BFD06 // GSM-7 payload ("Hello")
2. Delivery Receipt Requests
Set bit 6 (0x20) to request a delivery receipt. Often combined with the registered_delivery field:
ESM Class: 0x20 (binary 00100000) registered_delivery: 0x01 (request receipt)
3. Priority Messaging
Use bits 3-2 to prioritize messages. Example for urgent priority:
ESM Class: 0x10 (binary 00010000: Urgent priority)
Example SMPP PDUs
Example 1: Basic SMS (ESM=0x00)
0000001D // Command Length (29 bytes)
00000004 // Command ID (SubmitSM)
00000001 // Sequence Number
00 // Source TON
00 // Source NPI
736F7572636500 // Source Address ("source")
00 // Dest TON
00 // Dest NPI
36353433323100 // Destination Address ("654321")
00 // ESM Class (0x00: Default)
00 // Protocol ID (PID)
00 // Priority
00 // Schedule Delivery Time
00 // Validity Period
00 // Registered Delivery
00 // Replace-if-Present
00 // Data Coding (DCS=0x00)
00 // SM Default Message ID
07 // SM Length (7 septets)
C8329BFD06DDDF72 // Payload ("Hello!")
Example 2: Concatenated SMS (ESM=0x40)
00000025 // Command Length (37 bytes)
00000004 // Command ID (SubmitSM)
00000002 // Sequence Number
00 // Source TON
00 // Source NPI
736F7572636500 // Source Address ("source")
00 // Dest TON
00 // Dest NPI
36353433323100 // Destination Address ("654321")
40 // ESM Class (0x40: UDHI enabled)
00 // Protocol ID (PID)
00 // Priority
00 // Schedule Delivery Time
00 // Validity Period
00 // Registered Delivery
00 // Replace-if-Present
00 // Data Coding (DCS=0x00)
00 // SM Default Message ID
0C // SM Length (12 bytes)
0500030201C8329BFD06DDDF72 // UDH + "Hello" (Part 1/2)
Example 3: Delivery Receipt (ESM=0x20)
0000001D // Command Length (29 bytes)
00000004 // Command ID (SubmitSM)
00000003 // Sequence Number
00 // Source TON
00 // Source NPI
736F7572636500 // Source Address ("source")
00 // Dest TON
00 // Dest NPI
36353433323100 // Destination Address ("654321")
20 // ESM Class (0x20: Delivery receipt)
00 // Protocol ID (PID)
00 // Priority
00 // Schedule Delivery Time
00 // Validity Period
01 // Registered Delivery (receipt requested)
00 // Replace-if-Present
00 // Data Coding (DCS=0x00)
00 // SM Default Message ID
07 // SM Length (7 septets)
C8329BFD06DDDF72 // Payload ("Hello!")
Interactions with Other Fields
- UDHI (ESM) + DCS: If UDHI is set, ensure the DCS supports UDH (e.g., GSM-7 or 8-bit).
- ESM Class + registered_delivery: Use both to request delivery receipts explicitly.
- Priority Bits + Priority Flag: Some SMSCs prioritize messages based on ESM bits instead of the separate priority field.
Common Pitfalls
- Setting UDHI without including a valid User Data Header.
- Using delivery receipt flags (ESM=0x20) without setting
registered_delivery. - Mismatching ESM priority bits with the standalone
priority_flagfield.
Conclusion
The ESM class is a powerful tool for controlling message behavior in SMPP. Its bitmask design enables features like concatenation, receipts, and prioritization. Always verify SMSC support for advanced flags and test configurations thoroughly. For authoritative details, refer to the SMPP specification v3.4 or v5.0.
